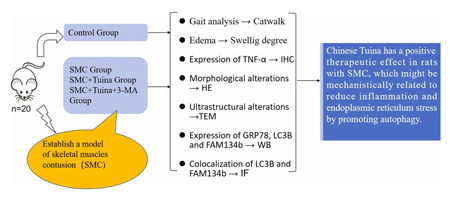
L’article intitulé « Le Tuina chinois améliore les lésions musculaires en régulant le stress du réticulum endoplasmique et l’autophagie dans un modèle de contusion musculaire squelettique chez le rat », publié dans Tissue and Cell le 25 mars 2025, examine les effets thérapeutiques du massage Tuina chinois sur la contusion musculaire squelettique (CMS), une blessure sportive courante caractérisée par une douleur musculaire localisée, un œdème, un hématome, une réduction de l’amplitude des mouvements et une inflammation.
Les traitements conservateurs traditionnels tels que le repos, l’application de glace, la compression et l’élévation échouent souvent à prévenir l’atrophie musculaire et la fibrose. Cette étude explore comment le massage Tuina influence le stress du réticulum endoplasmique (RE) et l’autophagie — deux voies critiques dans les processus de blessure et de réparation musculaires.
Dans l’étude, des rats atteints de CMS induite ont été traités par massage Tuina. Les résultats ont montré que le Tuina réduisait significativement les lésions musculaires et l’inflammation. Les effets thérapeutiques ont été attribués à la modulation des voies du stress du RE et de l’autophagie, suggérant que le massage Tuina facilite la réparation musculaire en régulant ces mécanismes cellulaires.
Ces résultats fournissent des preuves scientifiques soutenant l’efficacité du massage Tuina chinois dans le traitement des blessures musculaires, soulignant son potentiel en tant que thérapie non invasive pour favoriser la récupération musculaire via la régulation du stress du RE et de l’autophagie.
• Le Tuina chinois prévient les lésions musculaires chez les rats atteints de CMS.
• Le Tuina chinois régule l’expression de GRP78, FAM134 et LC3B.
• Le Tuina chinois pourrait inhiber l’inflammation et le stress du réticulum endoplasmique en favorisant…

METHODS
- Animaux expérimentaux
- Réactifs et anticorps
- Établissement du modèle de contusion musculaire squelettique (CMS) chez le rat >>>
- Traitement par Tuina chinois
- Évaluation de l’enflure du muscle gastrocnémien
- Analyse de la démarche
- Coloration H&E (hématoxyline-éosine)
- Analyse en microscopie électronique à transmission
- Analyse immunohistochimique (IHC)
- Analyse par Western blot
- Analyse en immunofluorescence
- Analyse statistique
Établissement du modèle de contusion musculaire squelettique (CMS) chez le rat

Establishment of rat SMC model and Chinese Tuina intervention. A: Establishment of rat SMC model(a, Self-made modeling device. b, SMC was induced by the falling of heavy objects; c, SMC appearance). B: Chinese tuina intervention (a, a pressure sensor was used to maintain consistent power; b, Chinese Tuina at the acupoints of SP6 and SP9).
Source : Article Link
RÉSULTATS
Le Tuina chinois a amélioré la démarche
chez les rats atteints de CMS.

Chinese Tuina improved gait in SMC rats. A: Stand time. B: Swing speed. C: Print area. Data were presented as mean ± standard deviation (n = 5). * P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.
Source : Article Link
Le Tuina chinois a atténué la réponse inflammatoire
chez les rats atteints de CMS.

Source : Article Link
Le Tuina chinois a amélioré la morphologie musculaire et la réparation de l’ultrastructure chez les rats atteints de CMS.

Source : Article Link
Le Tuina chinois a atténué le stress du réticulum endoplasmique et favorisé l’autophagie chez les rats atteints de CMS.

Chinese Tuina attenuated ERS and promoted autophagy in SMC rats. A and B: Protein levels of GRP78, FAM134b, and LC3II/GAPDH in skeletal muscle tissues were detected by Western blotting (n = 5). * P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.
Source : Article Link
DISCUSSION
Dans cette étude, nous avons examiné l’effet et le mécanisme potentiel du Tuina chinois appliqué aux points d’acupuncture SP6 et SP9 sur la contusion musculaire squelettique (CMS) chez le rat. Les principales conclusions sont les suivantes :
- 1) Le Tuina chinois améliore significativement la fonction motrice, réduit l’inflammation et accélère la guérison du muscle squelettique chez les rats atteints de CMS.
- 2) Le Tuina chinois diminue l’expression de GRP78, augmente l’expression de FAM134 et LC3, et renforce la co-localisation de FAM134 et LC3.
- 3) L’inhibiteur de l’autophagie 3-MA peut inhiber l’effet bénéfique du Tuina chinois sur la CMS chez le rat. Ces résultats révèlent que le Tuina chinois a un effet thérapeutique positif sur la CMS, et que son mécanisme d’action potentiel pourrait être la réduction de l’inflammation et du stress du réticulum endoplasmique par la promotion de l’autophagie.
CONCLUSIONS
L’étude intitulée « Le Tuina chinois améliore les lésions musculaires en régulant le stress du réticulum endoplasmique et l’autophagie dans un modèle de contusion musculaire squelettique chez le rat » conclut que le massage Tuina chinois réduit significativement les lésions musculaires et l’inflammation chez les rats atteints de contusion musculaire squelettique.
Les effets thérapeutiques sont attribués à la modulation des voies du stress du réticulum endoplasmique et de l’autophagie, ce qui suggère que le Tuina facilite la réparation musculaire en régulant ces mécanismes cellulaires.
Ces résultats apportent une preuve scientifique soutenant l’efficacité du massage Tuina chinois en tant que thérapie non invasive pour favoriser la récupération musculaire par la régulation du stress du réticulum endoplasmique et de l’autophagie.
The article titled “Chinese Tuina ameliorates muscle damage by regulating endoplasmic reticulum stress and autophagy in a rat model of skeletal muscle contusion,” published in Tissue and Cell on March 25, 2025, investigates the therapeutic effects of Chinese Tuina massage on skeletal muscle contusion (SMC), a common sports injury characterized by localized muscle pain, edema, hematoma, reduced range of motion, and inflammation.
Traditional conservative treatments like rest, ice application, compression, and elevation often fail to prevent muscle atrophy and fibrosis. This study explores how Tuina massage influences endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and autophagy—two critical pathways in muscle injury and repair processes.
In the study, rats with induced SMC were treated with Tuina massage. The results demonstrated that Tuina significantly reduced muscle damage and inflammation. The therapeutic effects were attributed to the modulation of ER stress and autophagy pathways, suggesting that Tuina massage facilitates muscle repair by regulating these cellular mechanisms.
These findings provide scientific evidence supporting the efficacy of Chinese Tuina massage in treating muscle injuries, highlighting its potential as a non-invasive therapy for promoting muscle recovery through the regulation of ER stress and autophagy.
• Chinese Tuina prevents muscle damage in SMC rats.
• Chinese Tuina regulates GRP78, FAM134 and LC3B expression.
• Chinese Tuina may inhibit inflammation and endoplasmic reticulum stress by promoting autophagy.

METHODS
- Experimental animals
- Reagents and antibodies
- Establishment of the rat SMC model >>>
- Chinese Tuina treatment
- Gastrocnemius muscle swelling evaluation
- Gait analysis
- HE staining
- Transmission electron microscopy analysis
- IHC analysis
- Western blotting analysis
- Immunofluorescence analysis
- Statistical analysis
Establishment of the rat SMC model

Establishment of rat SMC model and Chinese Tuina intervention. A: Establishment of rat SMC model(a, Self-made modeling device. b, SMC was induced by the falling of heavy objects; c, SMC appearance). B: Chinese tuina intervention (a, a pressure sensor was used to maintain consistent power; b, Chinese Tuina at the acupoints of SP6 and SP9).
Source : Article Link
RESULTS
Chinese Tuina improved gait in SMC rats

Chinese Tuina improved gait in SMC rats. A: Stand time. B: Swing speed. C: Print area. Data were presented as mean ± standard deviation (n = 5). * P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.
Source : Article Link
Chinese Tuina alleviated inflammatory response in SMC rats

Source : Article Link
Chinese Tuina enhanced muscle morphology and
ultrastructure repair in SMC rats

Source : Article Link
Chinese Tuina attenuated ER stress and
promoted autophagy in SMC rats

Chinese Tuina attenuated ERS and promoted autophagy in SMC rats. A and B: Protein levels of GRP78, FAM134b, and LC3II/GAPDH in skeletal muscle tissues were detected by Western blotting (n = 5). * P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.
Source : Article Link
DISCUSSION
In this study, we investigated the effect and potential mechanism of Chinese Tuina at SP6 and SP9 acupoints on SMC in rats. The major findings are as follows:
- 1) Chinese Tuina significantly improves motor function, reduces inflammation, and accelerates skeletal muscle healing in SMC rats.
- 2) Chinese Tuina downregulated GRP78 expression, upregulated FAM134 and LC3 expression, and enhanced FAM134 and LC3 co-localization.
- 3) Autophagy inhibitor 3-MA can inhibit the positive effect of Chinese Tuina on SMC in rats. These findings reveals that Chinese Tuina has a positive therapeutic effect on SMC in rats, and the potential mechanism of its treatment may be to reduce inflammation and ER stress by promoting autophagy.
CONCLUSIONS
The study titled “Chinese Tuina ameliorates muscle damage by regulating endoplasmic reticulum stress and autophagy in a rat model of skeletal muscle contusion” concludes that Chinese Tuina massage significantly reduces muscle damage and inflammation in rats with skeletal muscle contusion.
The therapeutic effects are attributed to the modulation of endoplasmic reticulum stress and autophagy pathways, suggesting that Tuina facilitates muscle repair by regulating these cellular mechanisms. These findings provide scientific evidence supporting the efficacy of Chinese Tuina massage as a non-invasive therapy for promoting muscle recovery through the regulation of endoplasmic reticulum stress and autophagy.
